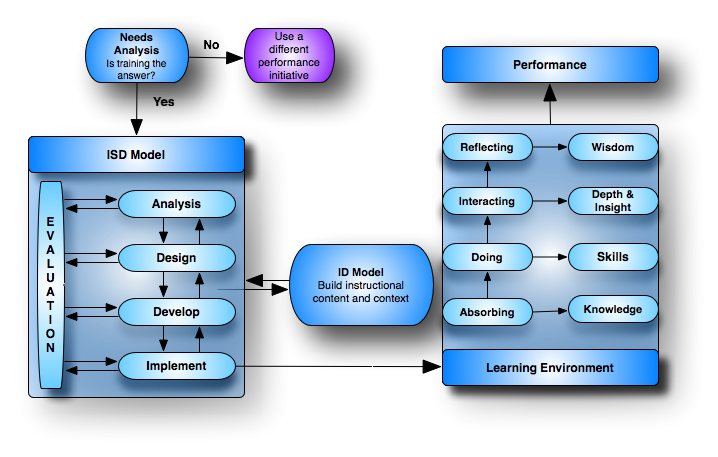
 ID and ISD ModelsThe main goal of an ID (Instructional Design) model or process is to construct a learning environment in order to provide the learners with the conditions that support the desired learning processes.ID models differ from an ISD (Instructional System Design) model in that ISD models are more broad in nature. On the other hand, ID models are less broad in scope and normally focus on the first two phases of the ISD model - analysis and design. They focus on the analysis of a to-be-trained skill or knowledge-acquisition and then convert the analysis into a training strategy (design of the learning environment). While ID models normally only account for analysis and design, ISD models normally cover five-phases:
Formative and Summative EvaluationsFormative evaluations are embedded in each of the five phases for judging the value or worth of that process while the program activities are "forming" or happening. This part of the evaluation focuses on the processes or activities. A summative evaluation is also performed at the end of the ISD process that focuses on the outcome (summation). |
http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/ahold/isd.html